2025 Guide: How to Choose the Right Solid State Phase Converter for Your Needs
When it comes to ensuring efficient power conversion for your electrical systems, selecting the right solid state phase converter is crucial. As technology continues to advance, the options available in the market grow more diverse, making it increasingly important for consumers to understand their specific needs before making a purchase. A solid state phase converter is designed to convert single-phase power to three-phase power, allowing users to operate three-phase equipment even in areas lacking adequate electrical infrastructure.
In this guide, we will delve into the factors you must consider when choosing the appropriate solid state phase converter. Whether you are looking to power industrial machines, tools, or other equipment, understanding the technical specifications, load requirements, and operational environments will help you make an informed decision. This comprehensive approach will not only optimize the performance of your machinery but also enhance energy efficiency and reliability, ensuring that your operations run smoothly and cost-effectively. Join us as we explore the key aspects of selecting the ideal solid state phase converter to meet your unique power transformation needs.

Understanding Solid State Phase Converters: Basics and Benefits
Solid state phase converters are increasingly recognized for their efficiency and reliability in converting single-phase power to three-phase power. Unlike traditional rotary converters, solid state versions utilize advanced electronic components, resulting in reduced maintenance requirements and improved performance. They operate quietly and can adapt to varying load conditions without compromising on power quality. According to a recent industry report by the Electrical Power Research Institute, solid state converters can achieve up to 95% conversion efficiency, making them an attractive option for various industrial applications.
When selecting a solid state phase converter, understanding your specific power needs is crucial. Consider factors like total horsepower required, the nature of the equipment being powered, and any potential voltage fluctuations in your area. It’s essential to choose a unit that not only meets but exceeds your operational demands to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
**Tips:** Always consult with a licensed electrician to assess your current electrical setup before making a purchase. Additionally, it’s advisable to look for models with built-in protection features, such as overload and surge protection, to safeguard your equipment from unexpected electrical issues. Lastly, reviewing user feedback and expert ratings can provide valuable insights into the reliability and performance of different options on the market.
2025 Guide: How to Choose the Right Solid State Phase Converter for Your Needs
This chart illustrates the benefits of using solid state phase converters versus traditional rotary converters. Data is based on reliability, efficiency, and user satisfaction ratings.
Types of Solid State Phase Converters: A Comprehensive Overview
When selecting a solid state phase converter, it's essential to understand the various types available to meet your specific requirements. Solid state phase converters generally fall into two primary categories: static and rotary. Static phase converters are typically more economical and are suited for applications where the load is relatively stable and does not require a full three-phase power supply throughout the operation. However, these converters may not be able to start larger motors or maintain performance under variable loads, which limits their application to smaller machinery or equipment.
On the other hand, rotary phase converters offer a more robust solution, providing balanced power for three-phase motors. They are capable of handling higher loads and ensuring a consistent and reliable power source, which is vital for equipment requiring a steady supply to operate efficiently. Rotary converters utilize both a motor and a transformer to create the required phase shift, making them an excellent choice for industrial applications where performance and uptime are crucial. Understanding the distinctions between these types can help you make an informed decision based on the specific demands of your machinery and power needs.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Solid State Phase Converter
When selecting a solid state phase converter, there are several key factors to consider to ensure it meets your needs effectively. First, determine the power requirements of your equipment. Assess the wattage necessary for operation, taking into account both the starting and running loads. It’s crucial to choose a converter that not only matches the total load but also can handle any potential surges when machines start up. A proper match ensures the longevity of your converter and the reliability of your connected devices.
Another important factor is the phase converter's capacity for efficiency and performance. Solid state converters are known for their superior efficiency compared to rotary converters. However, it's essential to consider the full-load voltage and response time. Look for models that can maintain stable voltage during operation, as this will help prevent damage to sensitive equipment. Additionally, evaluate the converter's installation requirements and ensure they align with your available space and electrical configurations. By carefully considering these elements, you can select a solid state phase converter that enhances your machinery’s performance and meets your operational demands.
2025 Guide: How to Choose the Right Solid State Phase Converter for Your Needs
| Key Factor | Importance Level | Description | Recommended Specifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | High | Ensure the converter can handle the total load required for your equipment. | Match to equipment wattage (e.g., 3 HP, 5 HP) |
| Voltage Compatibility | High | Ensure the converter works with your power supply voltage (e.g., 208V, 230V). | Match to existing facility voltage |
| Phase Conversion Type | Moderate | Choose between different types of phase converters (static, rotary). | Static for lower loads; rotary for higher performance |
| Space Requirements | Moderate | Determine the physical space available for installation. | Consider footprint size (e.g., compact models available) |
| Efficiency | High | Look for converters with high efficiency ratings to reduce energy costs. | Above 90% efficiency preferred |
| Noise Level | Low | Assess the noise levels of the unit to maintain a comfortable environment. | Units rated for quieter operation recommended |
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Solid State Phase Converters
When installing a solid state phase converter, the first step is to carefully select the location. Ideally, the converter should be placed in a dry, clean area with adequate ventilation to prevent overheating. Ensure the converter is mounted securely in a manner that minimizes vibration and movement, as these can lead to premature wear. Following the manufacturer’s guidance regarding spacing and clearance around the unit is also crucial. Proper wiring is essential for efficiency and safety; using the correct wire gauge and type will significantly enhance performance.
Maintenance of solid state phase converters plays a vital role in extending their lifespan and ensuring optimal functionality. Regularly inspect the connections for signs of wear or corrosion, and tighten any loose terminals to prevent resistance build-up. Dust and debris can accumulate over time, affecting performance, so periodic cleaning is important. It’s recommended to check the cooling fans and heat sinks to ensure they are working effectively, as overheating can lead to failure. Lastly, keep an eye on the output voltage and current levels to spot any irregularities early, allowing for prompt corrective action.
Common Applications and Use Cases for Solid State Phase Converters
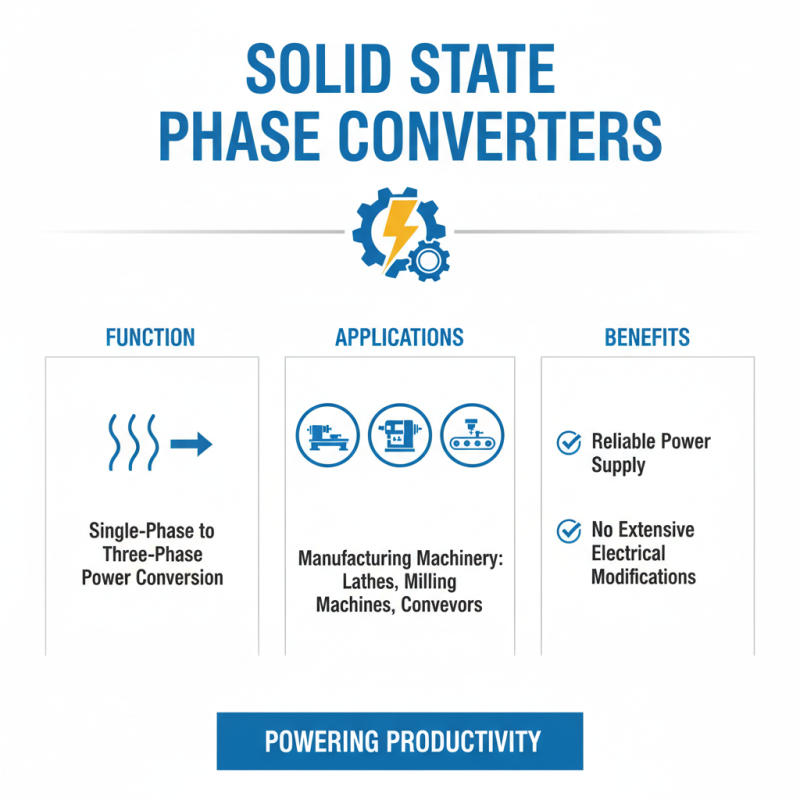
Solid state phase converters are essential for various applications, transforming single-phase power into three-phase power for equipment requiring more robust electrical input. One common application is in manufacturing facilities, where machinery such as lathes, milling machines, and conveyor systems rely on three-phase power to operate efficiently. These converters provide a reliable power supply, enabling manufacturers to maintain productivity and enhance workflow without the need for extensive electrical infrastructure modifications.
Another key use case for solid state phase converters is in agricultural settings. Farmers often depend on three-phase motors for irrigation systems, grain handling, and other equipment that optimize operations. By utilizing a solid state phase converter, they can effectively run their motors without incurring the high costs associated with installing three-phase power lines. This adaptability not only supports the agricultural industry’s efficiency but also ensures that farms can operate robustly with the electrical resources available in rural areas.
Overall, the versatility of solid state phase converters makes them an optimal solution for diverse environments, whether in industrial production or rural agricultural setups, ultimately facilitating more efficient use of tools and machinery across these sectors.
Related Posts
-

Step-by-Step Guide: How to Effectively Use a Single to Three Phase Converter in Your Projects
-

How to Seamlessly Upgrade from Single Phase to Three Phase Power Systems
-

Ultimate Guide to Understanding Phase Converters for 1 to 3 Power Conversion
-

Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Single Phase to Three Phase Converters in Modern Energy Systems
-

5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right VFD Phase Converter to Maximize Efficiency
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How Single to Three Phase Converters Transform Your Electrical Systems